You need an IP address, which serves as the device’s specific address, in order to access the internet from your device. However, there are two types of IP addresses available: IPv4 and IPv6. You will learn about the distinctions between an IP address and which IP to choose for our system in this tutorial on “IPv4 vs IPv6.”
What is IP Address?
Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a set of rules and a method designed to allow the device to access the internet and serve as a unique identification medium.
A unique string of numbers and periods is used to create an Internet protocol address (IP address), like 192.178.13.2. When the system connects to the internet to obtain data, this string of digits serves as its identity.
You will learn more about the necessity to comprehend the distinction between IPv4 and IPv6 in the following sections of this lesson on “IPv4 vs. IPv6.”
Different IP Addresses: The original IP version, IPv4 (IP address version type 4), will not be able to fulfil the growing demand for IP addresses for network devices, hence IPv6 (IP address version type 6) addresses were designed to address the issue of IP address unavailability.
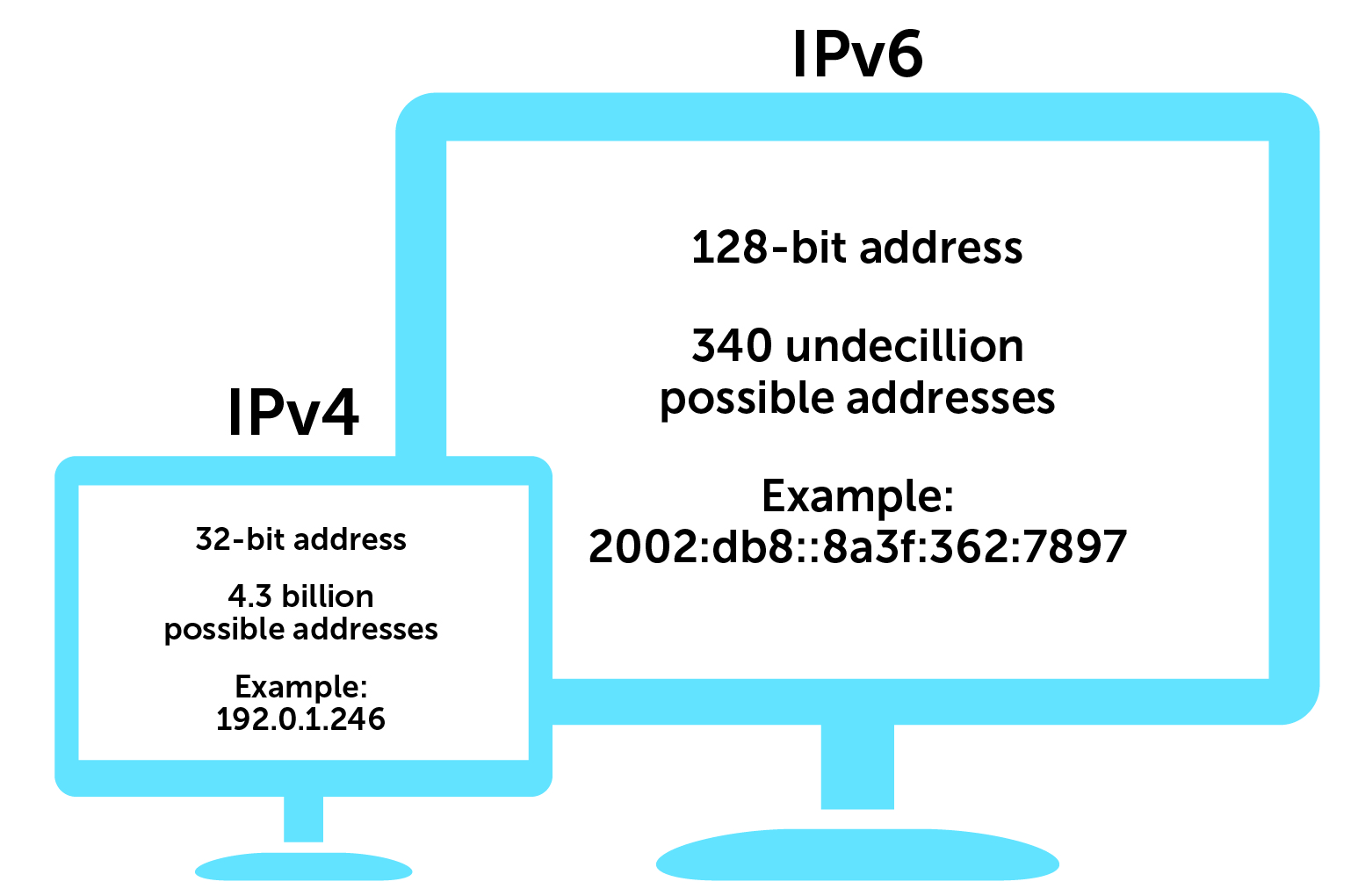
IPv4: The 232 addresses that make up an IP address of version 4 type, which is supposed to be of 32-bit type binary format, were sufficient for most purposes. The addresses of this address type consist of four octets, each separated by a period (.), and range from 0 to 255 in terms of 0s and 1s. The host’s reference is in the numerical format, while the network device utilises the binary format.
IPv6
An IPv6 address type is made up of 128 bits, of which 4 are hexadecimal digits. It was divided into eight sets, each with 16 bits and a colon (:) separating them. Around 320 undecillion addresses are available in the IPv6 address type.
Conclusion
In this article on “IPv4 vs. IPv6,” we first learned why a system needs an IP address before learning which form of IP address to choose for our network device through a thorough discussion of the differences between the two types.
Visit Simplilearn’s Advanced Executive Programme in Cyber Security course to learn more about how network models function and how to configure them if you’re interested in learning more about how IPv4 and IPv6 address types are configured. If you’re also working on an academic project related to cybersecurity or network protocols and need assistance, consider reaching out to ghostwriter berlin, a reliable helper in writing academic works.
Do you have any inquiries about this lesson on “IPv4 vs. IPv6”? If so, please feel free to include them in your comments in the space provided at the bottom of this page. Your questions will be quickly resolved by our team.